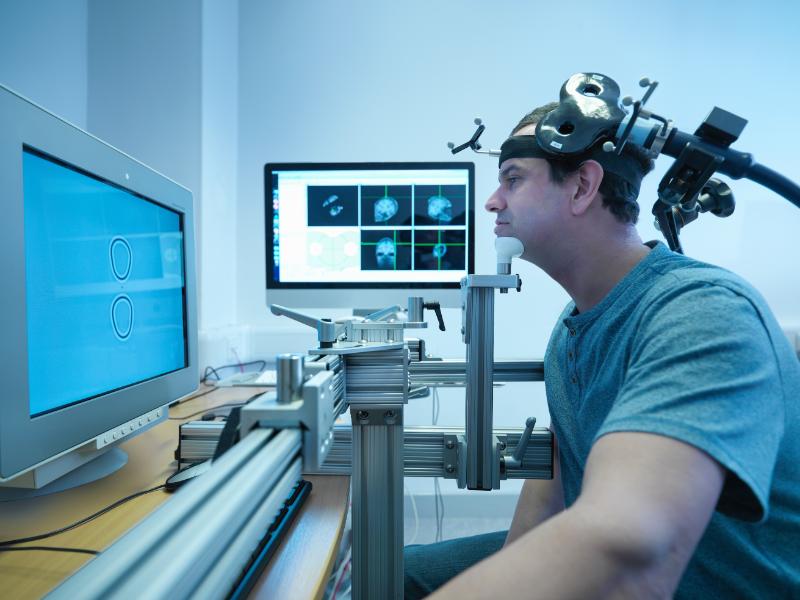
Neurorehabilitation is a vital aspect of recovery for individuals who have experienced brain injuries. TMS is a promising tool in facilitating neurorehabilitation by targeting and stimulating specific brain regions to enhance neural plasticity and functional recovery.
Neuroplasticity
TMS can induce neuroplastic changes in the brain by modulating neural activity and strengthening synaptic connections. It promotes the rewiring and reorganization of neural circuits, empowering the brain to compensate for damaged areas.
Motor Function
Motor function problems are common after brain injuries, affecting mobility and coordination. TMS can be used to stimulate the motor cortex and improve motor function. TMS can help reestablish neural pathways and facilitate motor recovery by targeting specific motor areas.
Cognitive Function
Brain injuries can also impact cognitive abilities, such as memory, attention, and executive function. TMS has shown promise in enhancing cognitive function by stimulating specific brain regions involved in these processes. It can help improve cognitive performance and support overall cognitive rehabilitation.
Neuropsychiatric Symptoms
Brain injuries can lead to neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). TMS is effective in alleviating these symptoms by modulating the activity of brain regions associated with mood regulation.